3. Digital 3D modelling as a part of artisan’s work
Digital 3D modelling software has come to involve the craft sector, and this has contributed to promoting a different way to configure and realize a project.
3Ddimensional modelling is the process of developing a mathematical representation of any surface of an object (either inanimate or living) in three dimensions via specialized software. The product is called a 3D model. Someone who works with 3D models may be referred to as a 3D artist. The model can also be physically created using 3D printing devices.
For more information on 3D modeling software, refer to Module 1: “Introduction to digital prototyping tech”.
The use of 3d software allows for an extraordinary reduction in the amount of time. For example, a virtual assessment made on a virtual model is easier and faster compared to traditional methodologies with real prototypes.
It is possible to intervene at any stage of the process without the amount of time needed by the traditional method.
Traditional Method
Handmade study → Real prototype

Image 3.1
Using 3D software
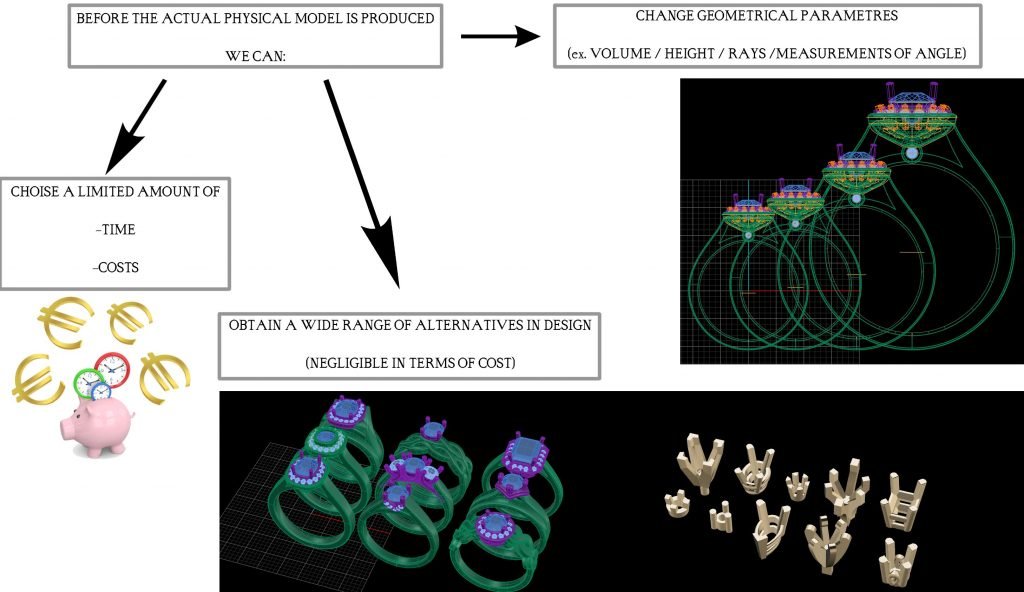
Image 3.2
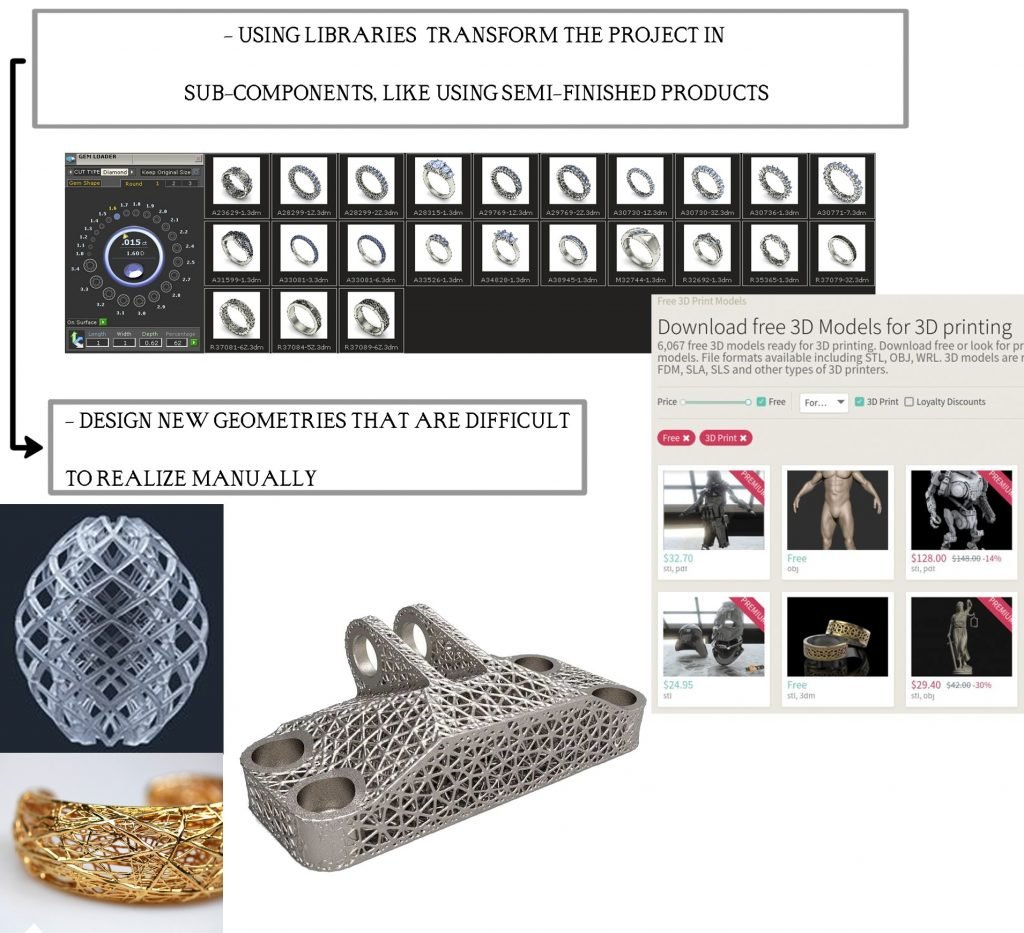
Image 3.3
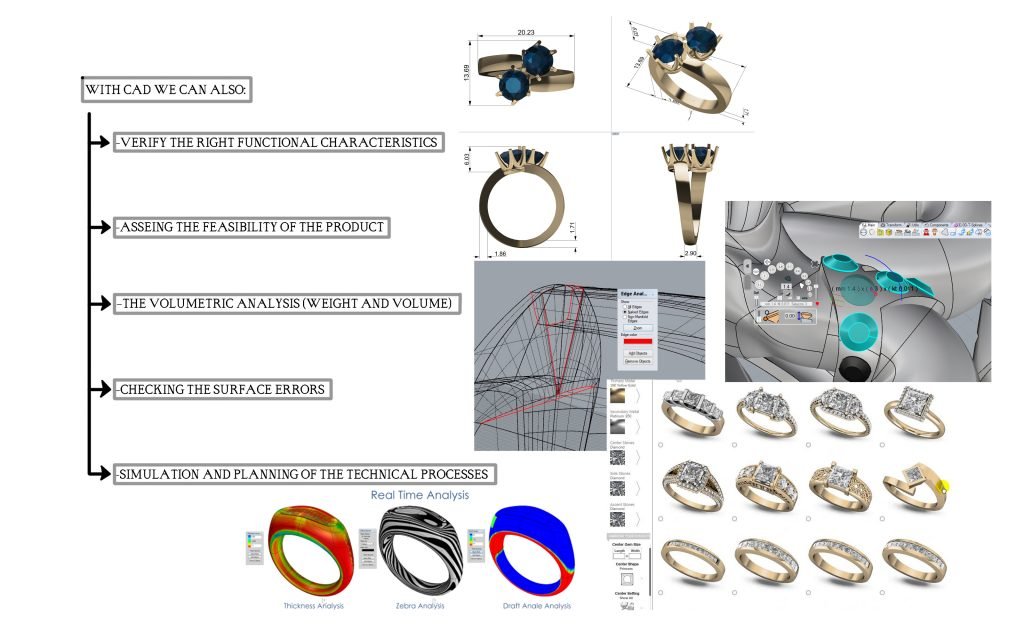
Image 3.4
Another feature that is achieved by using 3D software is the ease of communication and representation of the object through a rendering process called, indeed, “Rendering”.

Image 3.5

Image 3.6
Other software, not necessarily dedicated to 3D modeling, significantly improve the artisan production process, in particular, vector software for the use of laser equipment or software dedicated to scanning existing models. This discussion specifically concerns the use of 3D printers, so that, even if not directly dealing with them, the reader is invited to deepen these topics.